International projects
International projects STCU 5513
STCU 5513 Main results
Main results
Carbon incorporation in nanostructured silicon oxide matrix plays a key role in light emission mechanisms in all types of of SiO2:C materials. However the “magic” effect of carbon incorporation and local structure of light emitting sites are still unknown.
Por-SiO2:
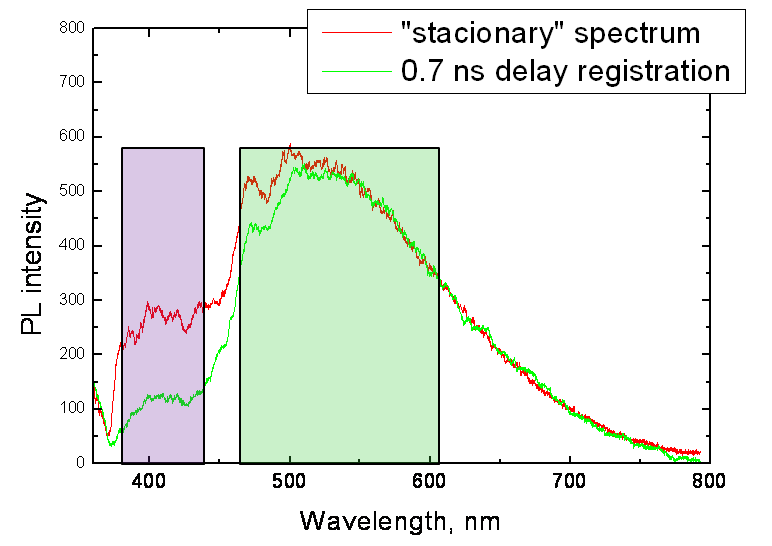
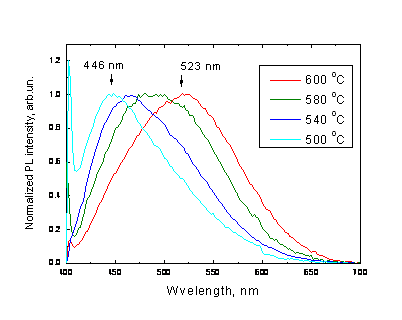
It was demonstrated that white-colour of such material can be varied from bluish-white to greenish-white. In case of por-SiO2:C blue component of PL is associated with light emission from defect states, while emission in green-orange spectral range is associated wit carbon. We have demonstrated that spectral properties of carbon related PL band can be tuned by tempeature of carbonization pretreatment (see figure below). We suggest that this efect is associated with „size“-effect, i.e. energy of optical transition is increasing with decreasing of avarage size of carbon nano-clusters.
|
Typical PL spectra of por-SiO2:C layers excited by N2 laser (337 nm) and measured by “stationary” regime and time-delay regimes |
|
|
|
|
a-SiO(x)C(y) thin films
Oxidation of a-SiC:H thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering was thoroughly studied in frame of the project. The effect of hydrocarbon source (methane v.s. acetylene) and oxidation ambient (oxygen, water vapor) was analyzed.
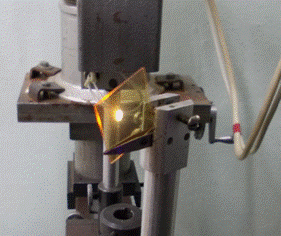
During the project we have developed “ultra-high-pressure” deposition regime, that allow to obtain strong white PL in as-deposited thin films without oxidation treatments (see photo).
|
Typical image of light emission from as-deposited a-SiO(x)C(y):H thin films on the glass substrate |
|
|
SiO2:C powders
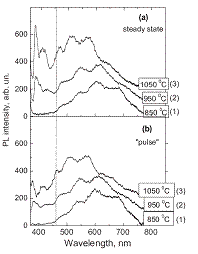
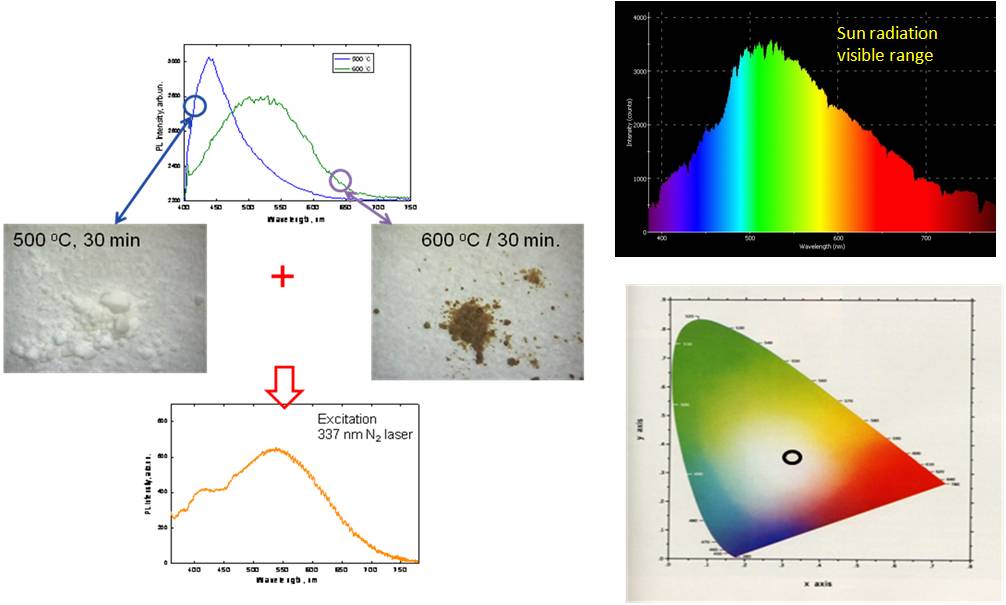
We have found the “size-effect” in SiO2:C powders, similar to that observed in porous SiO2:C layers (see figure)
|
Spectral shift of PL band in SiO2:C powders as a function of annealing temperature |
|
|
We have demonstrated that color properties of emission light can be easily tuned to desired simply by mixing powders annealed at different temperatures.
|
“Color engineering” by combination of SiO2:C powders annealed at different temperature |
|
|
Back to Top 
|